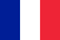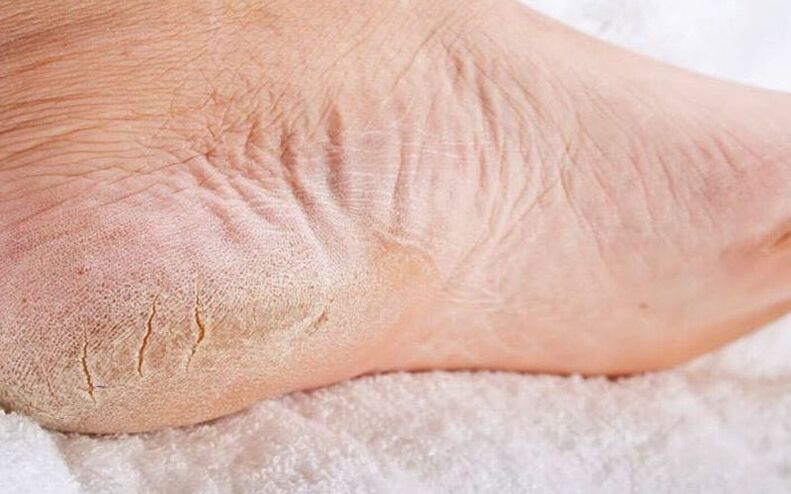
Fungal infections often affect the toes or nails. This disease affects adults and children. To prevent the pathology from becoming chronic, you need to know the symptoms of athlete's foot and what such a disease looks like.
The main symptoms of the disease
Mycosis of the feet is the most common among all skin diseases. You can get sick if you ignore basic hygiene rules. Fungi are sometimes very difficult to treat.
For each person, foot fungus begins and develops in its own way. The most common signs by which you can recognize athlete's foot are:
- characteristic cracks appear between the toes;
- You can tell that a fungus has appeared on your feet and between your toes with characteristic itching;
- the skin of the feet is very dry, often flaky and rough;
- blisters appear between the fingers, burst when destroyed;
- the infection may spread to neighboring areas;
- red spots appear on the skin, which causes significant discomfort;
- You can also recognize athlete's foot by its unpleasant smell.
When the first signs of the disease appear, you should immediately consult a dermatologist. If you do not do this in advance, it will be more difficult to treat the fungus.
Fungal symptoms depending on the type of pathogen
This disease develops due to various types of pathogens. The symptoms of a foot injury will vary from case to case.
- If yeast fungus forms on the feet, the nail becomes thinner and peels off from the bed. The skin of the foot is hyperemic (gets a red color).
- With the development of epidermophytes, the nail turns yellow and is covered with spots. The skin on the feet peels off and gives off an unpleasant smell. A characteristic sign of this type of fungus is increased dryness of the skin.
- When mold fungus appears, the nail plate can suddenly change color. If the pathogen gradually spreads to the entire leg, the skin becomes red. A person is bothered by itching, the skin may crack. In this case, pain and other unpleasant sensations appear during walking.
Only a doctor can determine the type of pathogen. This cannot be done at home. If you self-medicate, you can only harm yourself. Your feet will suffer from this and the skin fungus will spread more and more.
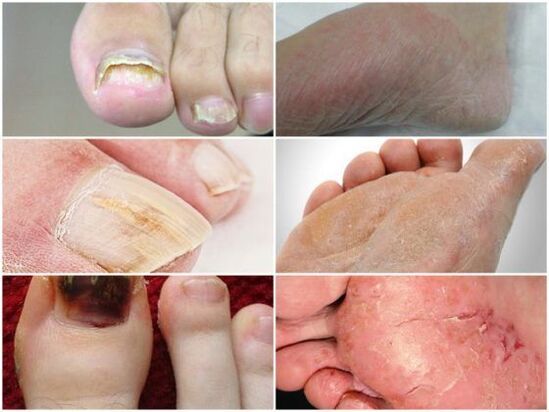
Symptoms of some forms of fungi
Depending on the affected area and the degree of development, several forms of pathology are distinguished. Each has different symptoms. By knowing the first signs of foot disease, you can start treating mycosis in time.
- Interdigital dermatophytosis is the most common stage of the disease. Feet are more active in spring and summer when they sweat the most. Cracks and sores appear between the fingers. You can see the presence of scales on their skin. The leg looks completely healthy. Often a person feels itching.
- The deleted form appears to the least pronounced degree. Peeling is noticeable between the fingers. At this stage of the disease, a sharp unpleasant smell is emitted from the feet: it appears to be due to increased bacterial activity.
The disease can occur in different forms. Let's get acquainted with their symptoms, so that we know how to determine the fungus on the feet and, if it develops, start treatment. It should be remembered that in the advanced stages of the disease, the nail is completely destroyed. It is almost impossible to restore it.
Squamous type
This fungus is characterized by intensive peeling of the epidermis. Moreover, the skin areas between the toes and the sides of the foot are the most intensively affected. There are no signs of an inflammatory process. In the photo of the first signs of athlete's foot, areas of hyperemia are noticeable. Squamous fungus looks like this:
- stratum corneum thickens;
- skin shines, sometimes thickens;
- the pattern on the skin becomes clearer;
- the fungus gradually spreads to the fingers, the whole foot and affects the nails;
- sometimes lamellar scales appear on the epidermis;
- The patient does not feel any other unpleasant sensations.
Dyshidrotic type
With this fungus, small blisters filled with fluid are formed on the skin. They are usually on the side of the leg. Then they gradually move to the inner side of the fingers. How to recognize the fungus on dyshidrotic feet:
- the bubble is usually single, but if there are many of them, they merge into one big one;
- if left untreated, the liquid in the blisters gradually darkens;
- If the blister ruptures, crusted erosion appears in its place.
With this type of athlete's foot, the risk of bacterial infection is very high. Infection enters the body through open skin lesions.
Intertriginous type
This type of mushroom is the most common. At first, a person does not feel any symptoms. Up to a certain point, the skin of the toes does not change. Later, cracks and layers appear. The skin is not affected, but may sweat.
Candidiasis of the feet
The characteristic symptoms of this fungal infection are as follows:
- the lesion is the 3rd or 4th finger;
- the skin becomes red and swollen;
- There is a blister around the lesion where the peeled layer of skin is;
- There are pustules and blisters nearby.
If a bacterial infection enters the affected area, it causes an increase in local temperature. Swelling is noticeable in the skin of the legs. In severe cases, a person experiences general hyperthermia.
Symptoms of nail fungus infection
A person's toenails can also be affected. The disease can be distinguished by the following symptoms.
- Noticeable change in the color of the nail plate. Depending on what type of pathology the patient has, the nail takes on different shades. Sometimes it can change only in one part of the nail plate.
- Broken nails. This happens only in advanced stages. If the nail is completely infected, it is destroyed.
- Changes in nail structure.
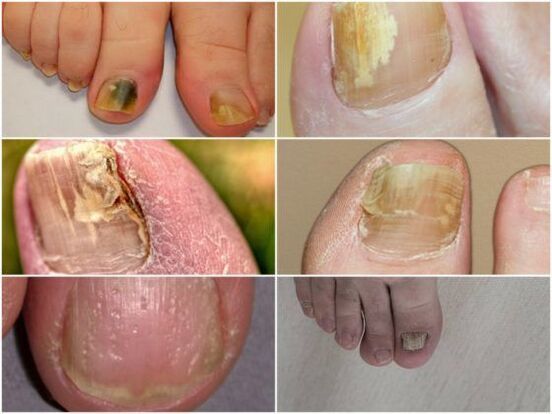
There are several types of onychomycosis, a fungal infection of the nails.
- Atrophic appearance. The nail plate looks very thin. It becomes dark, sometimes acquires a gray-brown color. It gradually peels off from the nail bed. It becomes keratinized and loosens under the skin.
- With the normotrophic form of the foot fungus, the plate changes its shade. Spots appear on it - white, yellow, green and even black. The nail structure is not affected.
- In the hypertrophic form, the plate gradually thickens and becomes porous. The affected area looks very uncomfortable and in some cases causes pain when walking. It crumbles and crumbles untreated on the sides.
Some types of onychomycosis
Depending on the degree of spread of the disease, its forms are distinguished.
- Lateral onychomycosis is the most common. A small yellow spot first appears on the free edge of the nail. In the future, you will see how it increases and the nail plate thickens. A person feels discomfort while walking. The spread of an unpleasant smell is noticeable. Treatment of lateral onychomycosis is difficult.
- Superficial onychomycosis is characterized by damage to only the upper layers of the plaque. It does not harden, but over time it becomes chalky.
- The rarest form of the disease is subungual onychomycosis. The skin in the nail layer becomes noticeably thicker. The nail turns white and loses its transparency.
General principles of treatment
Any treatment of pathology begins with diagnosis. Only then can a suitable remedy be prescribed. Self-medication usually leads to deterioration of the condition of the feet. Let's get acquainted with the most common therapy methods.
- At the first signs of fungal infection, special varnishes, plasters, ointments and sprays are used. They should be used for a long time and according to the instructions.
- If local therapy is ineffective, complex antifungal drugs are prescribed. They are used orally.
- Surgical removal of the affected nail.
- Laser therapy.
- In advanced forms of the disease, systemic drugs are prescribed.
You can prevent the occurrence of an unpleasant disease by following the rules of hygiene. You should avoid using other people's personal hygiene products (towels, slippers). When the first symptoms of the disease appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Types of mycosis
Fungal infections of the feet usually appear between the toes. It is caused by several types of fungi. This problem is most common in adults, as children's sweat can neutralize the fungus.
Mycotic lesions can be of different types:
- candidiasis - occurs when the body's resistance decreases, mostly in women;
- epidermophytosis is only a "male" disease that develops due to excessive sweating;
- Rubromycosis is a highly contagious form that can occur even in young children.
Symptoms and forms of the disease
Symptoms of fungal infection can vary depending on the age of the patient, the state of the immune system and the nature of the blood circulation.
In a person with strong immunity, the fungus can remain on the skin for several months without showing itself. Mild itching and mild redness of the skin may occur.
Treatment and best remedies

Advanced mycosis is treated with fungicidal tablets and antimycotic ointments. The latter are used after washing and drying the feet.
Folk remedies are recommended to be used only in the initial stage of the disease, as well as to eliminate itching. They should be used with extreme caution, as some are based on cauterization of the skin and can cause burns.
As for traditional medicine, they are used at the patient's own risk. Be especially careful when using formulas that contain vinegar, celandine or manganese, as this can cause skin burns.
In parallel with drug treatment, you can use baths with oak bark, chamomile or sage. Soda bath effectively reduces itching.
Preventive measures
Although there are effective and inexpensive treatments for foot fungus on the market, it is better not to let the problem develop. Prevention of fungal infection consists of the following:
- daily hygiene;
- wearing individual shoes (especially in public showers, baths and swimming pools);
- regularly treat the inside of shoes with ammonia;
- daily change of socks;
- strengthen and maintain immunity.
These are basic, simple actions that anyone can take. However, if infection occurs, to prevent relapse, it is necessary to treat foot fungus with drugs for another 14 days after all symptoms of mycosis have completely disappeared.
Toenail fungus: symptoms and treatment, photo of toenail fungus
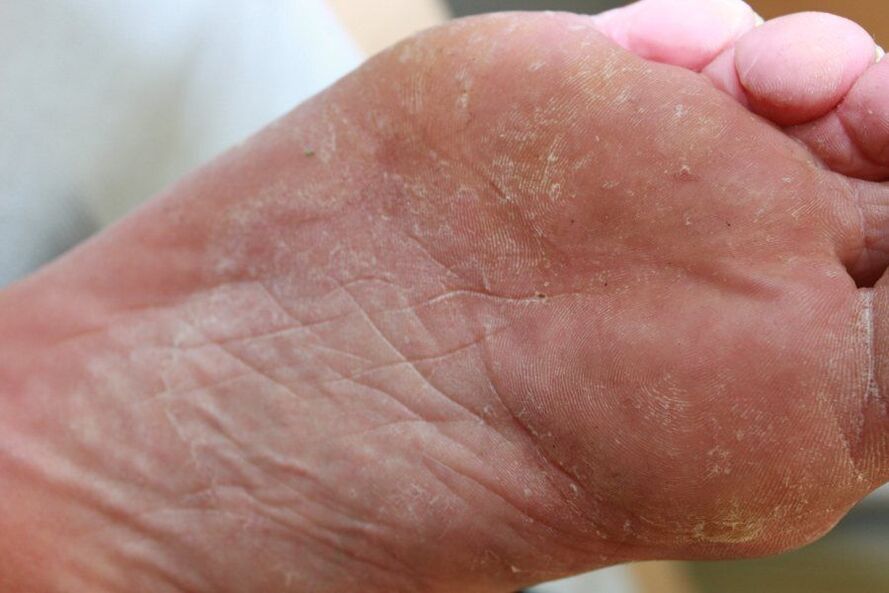
Athlete's foot is one of the most common diseases in dermatological practice. It occurs primarily in cultures where it is customary to wear shoes, and affects up to 70% of the adult population.
Most often, foot fungus is observed in the elderly, as well as in people with significantly weakened immunity, for example, with diabetes, AIDS, blood circulation disorders of the lower extremities and other diseases of this type.
Often, the term "fungus or mycosis of the foot" refers to the damage of the fungal mycelium to the plantar skin of the feet, nails and interdigital spaces.
Pathogens
Among the many types of fungi, the main causative agent of mycosis of the foot is the following:
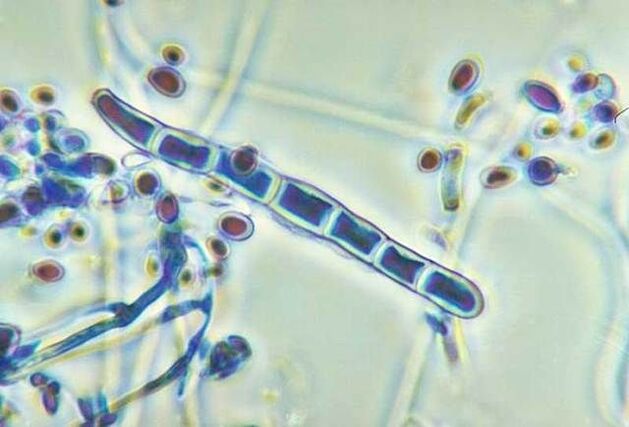
- Trichophyton rubrum,
- Trichophyton mentagrophytes,
- Epidermophyton floccosum.
Other causes of fungal infections of the feet, which are not so common:
- Trichophyton tonsurans, the causative agent of mycosis in children in America,
- candida,
- Scythalidium hyalinum,
- Scythalidium dimidiatum.
All pathogens of fungal infections are adapted to parasitize in the stratum corneum of the skin, producing special enzymes that break down keratin. In addition, their membranes (cell walls) contain mannans - special substances that suppress local immunity and contribute to the development of chronic inflammation.
Ways of infection and factors that cause the disease
It is believed that some species of athlete's foot can survive for up to a year in flakes of exfoliated skin. To become infected with a fungus, it is enough for such skin flakes to stick to the feet with the pathogen, and then fall into favorable conditions for reproduction: humidity and heat.
The most common infections with athlete's foot occur:
- In public places: bathrooms, beach beds, swimming pools, saunas, even just beach sand.
- In the family: common household shoes, lack of personal towels for feet, low level of hygiene.
- Habits: change shoes, socks, put on someone else's shoes (for example, house slippers of the hosts when guests come).
Factors that cause infection:
- Reduction of local protective forces as a result of circulatory disorders (for example, vasculitis, obliterating atherosclerosis of the lower extremities), some chronic diseases (HIV, other immunodeficiency conditions, diabetes, etc. ).
- Prolonged sweating of the feet during long workouts in athletes, when wearing closed or poorly ventilated shoes in the summer.
- Cracks and macerations in the skin of the feet.
In general, men get sick more often than women, and the frequency of fungal infections of the feet increases with age. Risk group for fungal infections of the feet:
- miners,
- military,
- bathroom staff,
- regular baths and saunas,
- athletes.
Types of disease
According to the location of the pathological focus of the skin on the leg affected by the fungus:
- Interdigital mycosis (dermatophytosis). It is most often observed in chronic (squamous) or acute (intertriginous) forms.
- Plantar mycosis. It often manifests itself as peeling and keratinization of the skin of the feet.
- Dyshidrotic dermatophytosis. Bubbles and vesicles appear on the skin of the feet, often reminiscent of allergic dermatitis.
- Deep mycosis. At this time, not only the surface, but also the deep layers of the skin are affected.
- Onychomycosis. Fungal infection of the toenails.
Depending on the type of pathogen, the main fungal diseases of the feet are:
- Athlete's disease caused by Trichophyton mcntagrophytes.
- Rubrophytosis caused by Trichophyton rubrum.
Rubrophytosis of the feet: the main types and symptoms
Rubrophytosis is the most common fungal foot disease. It happens in almost 70-90% of cases.
Symptoms
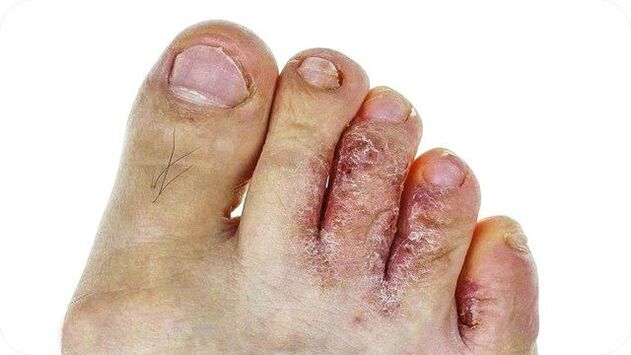
The classic form of rubrophytosis is characterized by redness and moderate thickening (lichenification) of the skin. The affected skin is a dry surface with a shiny, developed pattern, flour-like scales accumulated in the area of grooves and folds.
Usually, the disease begins with the third or fourth interdigital layer, which is the densest. The fungus then spreads to other spaces between the toes, the plantar part, and the back of the foot.
The following forms are characteristic of rubrophytia:
Commonly encountered:
- squamous form (the main symptom is scaly skin),
- keratinizing form - the presence of "corns", thickenings.
- intertriginous (opreloid),
- dyshidrotic (with the formation of blisters),
- mixed form (diaper rash, blisters).
On the leg
Deleted squamous rubrophytia has the least noticeable symptoms and is almost not noticed by the patient. Its main symptoms are:
- Interdigital spaces: crusting, the presence of flour-like scales, small cracks on the surface.
- There are practically no complaints, or a small itch may bother you.
In this form, rubrophytosis can last quite a long time. However, the progression of the disease is observed gradually, which leads to the appearance of hyperkeratotic and mixed forms. Gradually there are:
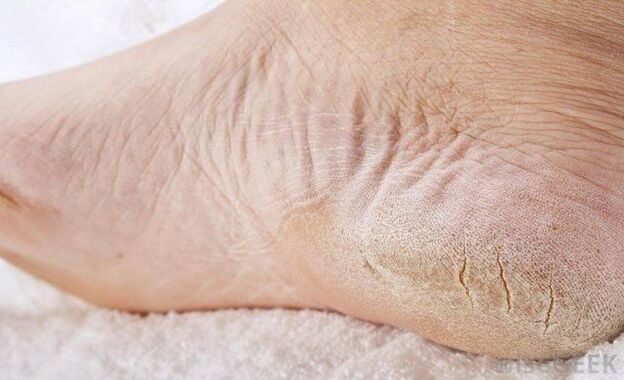
- increased dryness of the skin of the feet,
- roughening of the skin,
- the appearance of rough calluses on the bottom and sides of the foot,
- formation of deep and painful cracks in the heel area.
There are 3 main types of skin peeling with rubrophytosis of the feet:
Floury. The natural folds and furrows of the skin look like they are sprinkled with flour.Ring-shaped . Reddened spots with fringes of eroded epithelium.Large layered . In this case, the skin is peeled off in large slabs.
In the interdigital spaces
During intense sweating of the feet, wearing poorly ventilated shoes or inadequate treatment, the spaces between the toes begin to get wet from time to time. The skin swells, erodes, and deep cracks form. At this stage, the main complaints of patients are itching, pain, burning.
In the absence of timely and effective treatment, the process gradually worsens, which is manifested by pain and itching, which is aggravated by movement. Large blisters form on the skin of the interdigital spaces and on the lateral surfaces of the fingers, which later turn into erosion and are surrounded by a border of whitish epidermis.
On nails
Nail plates of the toes with rubrophytosis:
- thickened
- falling apart
- yellowish-gray or brown,
- white spots that later spread to the entire nail.
Sometimes it separates from the nail bed, thickens and takes on the appearance of a bird's claw or sunken nail, which causes additional discomfort for patients.
Complications of rubrophytosis
As a rule, rubrophytia spreads to other parts of the body: hands, smooth skin, vellus hair. The pathogen enters new areas of the skin by lymphogenous, as well as by contact (for example, transferred by hands when washing feet).
- Hands - damage to palms and nails.
- Smooth skin - lesions on the face, inguinal-femoral folds, hips, legs.
In this case, mycosis manifests itself in the form of round pink-red or pink spots that tend to merge and grow peripherally. Their surface is covered with scales and along the edges there is an inflammatory ridge with small bubbles and crusts.
If rubrophytia has spread to large folds, itching occurs.
Athlete's foot: types and symptoms
Athlete's foot occurs less often than rubrophytosis and has the same forms of the disease:
- Deleted.
- keratinizer.
- Diaper rash.
- With the formation of bubbles.
- Athlete's nails.
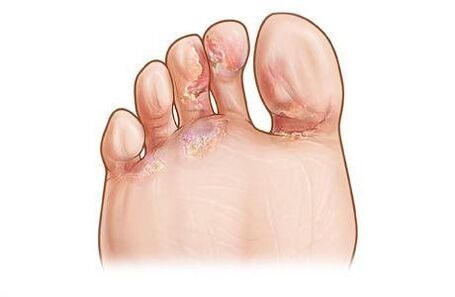
Then, plaque-like thickenings of bluish-red skin appear on the lateral surfaces and the bottom of the leg. There are scales in the center of the rash, the boundaries of the lesions are clear. In the spaces between the fingers, the epidermis acquires a whitish color.
Patients with athlete's foot are bothered by itching, increased dryness and soreness of the skin.
Opreloid (intertriginous) form of epidermophytosis is characterized by redness, swelling and maceration of interdigital folds. Cracks are often formed and pain is felt.
When the pathogen affects the arch of the foot, a dyshidrotic form can often be observed with the formation of pink or red wet erosion-like blisters after opening.
Athlete's foot occurs most often in the big toe (I) and little toe (V). In the thickness of the nail, near the free edge, yellowish spots and stripes are formed, which gradually increase and cover the entire nail. Then, the nail begins to collapse, sometimes peeling from the nail bed.
Acute epidermophytosis Podvysotskaya
The main symptoms of this form of athlete's foot:
- swelling of feet, fingers,
- multiplicity of vesicles,
- weeping erosions,
- maceration of interdigital folds,
- enlarged inguinal lymph nodes,
- increase in body temperature,
- Headache,
- difficulty walking due to pain,
- general weakness.
Onychomycosis of the toes: symptoms and types
In addition to the causative agent of rubrophytosis and epidermophytosis, onychomycosis can be caused by yeast fungi of the genus Candida, as well as some other fungi.
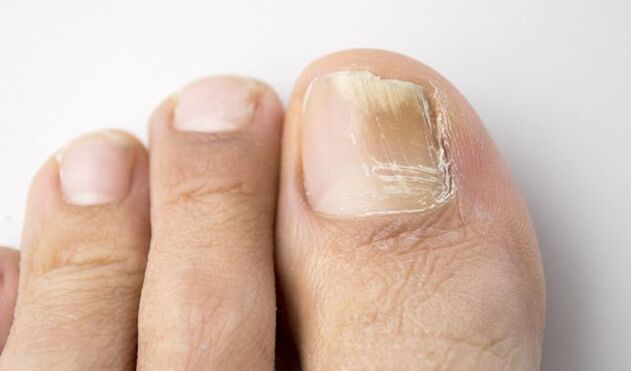
The most typical symptoms of onychomycosis, which begins near the free edge of the nail:
- discoloration, loss of natural brightness,
- thickening of the nail plate,
- formation of subungual hyperkeratosis,
- destruction of the nail, detachment from the nail bed.
There are 2 main types of nail damage with onychomycosis:
- Normotrophic: white and yellowish stripes appear in the thickness of the nail.
- Atrophic: thinning, destruction of the nail plate, its separation.
Diagnosis of fungal infections of the feet
A specialist in the treatment of fungal infections of the feet is a dermatologist who, if necessary, can involve other specialists in the treatment.
After talking with the patient, clarifying the complaints and the characteristics of the occurrence and course of the disease, the doctor will examine the affected surface and prescribe some additional types of examination, for example:
- Microscopic examination with additional treatment of the material with potassium hydroxide.
- Examination of Wood's lamp.
- Inoculation of suspected biological material in special media for the development of fungi, as well as in media for bacteria.
Treatment
Treatment for any fungal infection of the foot should be prescribed by a doctor to achieve a complete cure.
In general, the treatment of foot mycoses is based on the following principles of therapy:
- Fighting the infectious agent. In the initial stages of the disease, local drugs are usually prescribed - antifungal ointments, creams, lotions. In severe cases, use systemic antifungal agents.
- Increasing immunity and improving local blood circulation, treatment of the main disease.
- Sensitization therapy. Since mycosis of the feet is often accompanied by allergic reactions, antiallergic drugs are prescribed accordingly to help improve the patient's condition.
Treatment at home
- To effectively treat mycosis of the feet, it is necessary to remember that fungi multiply in a moist environment. By excluding moisture, the fungus will not develop and the chances of cure will increase.
- Protect your family members from fungal diseases. You have to explain to them that from now on you can't walk barefoot in the apartment, especially in the bathroom or shower. After taking a bath or shower, it is necessary to treat the bath itself, the tray and the floor with a disinfectant.
- Wash your feet with soap every day, collect all the fallen pieces of skin with a napkin so that nothing gets under the nails.
- After washing your feet, be sure to dry the spaces between your toes with toilet paper or a hair dryer, and then apply an antifungal agent prescribed by your doctor. Treatment should be continued for several months even in cases where the manifestations of mycosis have completely disappeared.
- Use powder when wearing shoes.
- Wear white cotton socks (clean them daily). Used socks should be boiled for 10 minutes or soaked in disinfectant. Shoes should be disinfected with antifungal sprays.
Prevention of foot mycosis
Timely treatment of diseases that can reduce the body's defenses or disrupt blood circulation.
The result
Athlete's foot is one of the most common fungal skin infections. In most cases, following simple rules of prevention helps prevent the disease, and timely treatment begins to completely get rid of mycosis.